This site uses cookies to provide logins and other features. Please accept the use of cookies by clicking Accept.
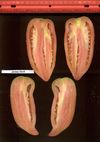
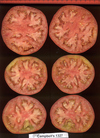
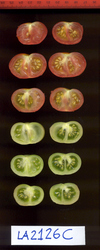
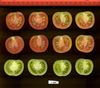
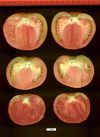
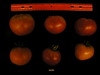
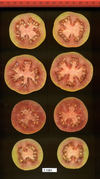
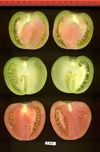
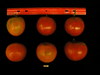
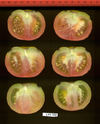
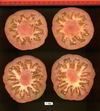
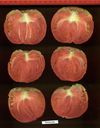
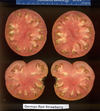
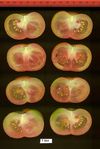
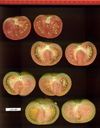
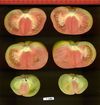
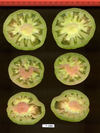
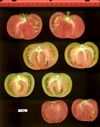
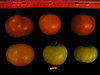
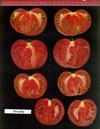
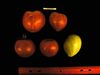
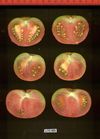
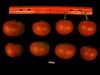
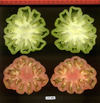
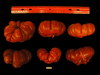
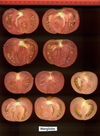
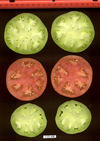
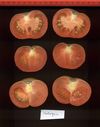
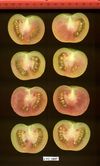
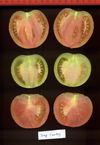
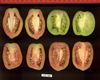
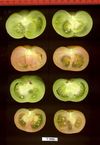
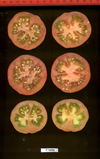
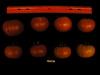
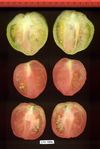
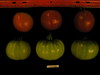
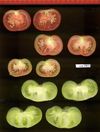
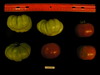
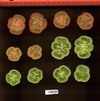
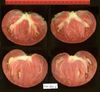
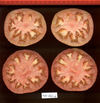
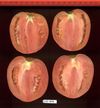
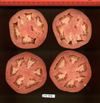
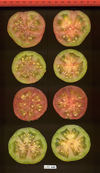
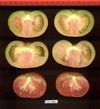
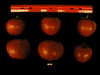
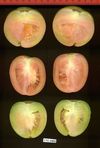
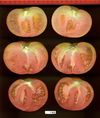
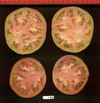
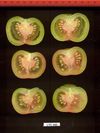
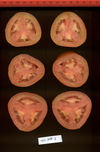
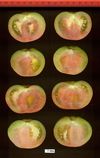
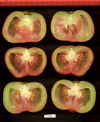
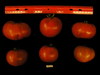
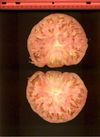
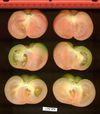
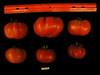
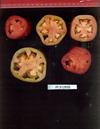
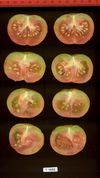
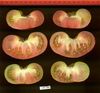
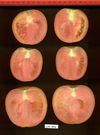
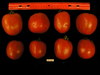
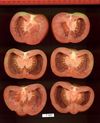
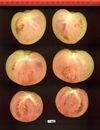
Tomato locus Locule number
| Locus details | Download GMOD XML | Note to Editors | Annotation guidelines |
[loading edit links...]
|
[loading...]
|
|
 Links to external databases Links to external databases
 Links to external databases Links to external databases
|
| Registry name: | None | [Associate registry name] |
 Notes and figures (0) Notes and figures (0)
 Notes and figures (0) Notes and figures (0)
| [Add notes, figures or images] |
Success
The display image was set successfully.
| Image | Description | Type |
|---|
 Accessions and images (143) Accessions and images (143)
 Accessions and images (143) Accessions and images (143)
| [Associate accession] |
Accession name:
Would you Like to specify an allele?
| Opalka |  |  |  |  |  | |
| Howard German |  |  |  |  |  | |
| Polish Giant Paste |  |  |  |  |  |
See 140 more accessions
LA1388 LA0172
 Alleles (2) Alleles (2)
 Alleles (2) Alleles (2)
| [Add new Allele] |
 Associated loci (0) Associated loci (0)
 Associated loci (0) Associated loci (0)
| [Associate new locus] |
[loading...]
|
| Associated loci - graphical view | None |
 SolCyc links SolCyc links
 SolCyc links SolCyc links
|
[loading...]
 Sequence annotations Sequence annotations
 Sequence annotations Sequence annotations
|
| Genome features | None |
 Gene model matches Gene model matches
 Gene model matches Gene model matches
|
 SGN Unigenes SGN Unigenes
 SGN Unigenes SGN Unigenes
| [Associate new unigene] |
Unigene ID:
[loading...]
 GenBank accessions GenBank accessions
 GenBank accessions GenBank accessions
| [Associate new genbank sequence] |
JF284938 Solanum lycopersicum var. cerasiforme cultivar Cervil locule number quantitative trait locus genomic sequence.
JF284939 Solanum lycopersicum cultivar Levovil locule number quantitative trait locus genomic sequence.
JF285114 Solanum lycopersicum cultivar Arava locule number quantitative trait locus genomic sequence.
JF284939 Solanum lycopersicum cultivar Levovil locule number quantitative trait locus genomic sequence.
JF285114 Solanum lycopersicum cultivar Arava locule number quantitative trait locus genomic sequence.
| Other genome matches | None |
 Literature annotations [2] Literature annotations [2]
 Literature annotations [2] Literature annotations [2]
| [Associate publication] [Matching publications] |
Distribution of SUN, OVATE, LC, and FAS in the Tomato Germplasm and the Relationship to Fruit Shape Diversity.
Plant physiology (2011)
Show / hide abstract
Show / hide abstract
Phenotypic diversity within cultivated tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) is particularly evident for fruit shape and size. Four genes that control tomato fruit shape have been cloned. SUN and OVATE control elongated shape whereas FASCIATED (FAS) and LOCULE NUMBER (LC) control fruit locule number and flat shape. We investigated the distribution of the fruit shape alleles in the tomato germplasm and evaluated their contribution to morphology in a diverse collection of 368 predominantly tomato and tomato var. cerasiforme accessions. Fruits were visually classified into eight shape categories that were supported by objective measurements obtained from image analysis using the Tomato Analyzer software. The allele distribution of SUN, OVATE, LC, and FAS in all accessions was strongly associated with fruit shape classification. We also genotyped 116 representative accessions with additional 25 markers distributed evenly across the genome. Through a model-based clustering we demonstrated that shape categories, germplasm classes, and the shape genes were nonrandomly distributed among five genetic clusters (P < 0.001), implying that selection for fruit shape genes was critical to subpopulation differentiation within cultivated tomato. Our data suggested that the LC, FAS, and SUN mutations arose in the same ancestral population while the OVATE mutation arose in a separate lineage. Furthermore, LC, OVATE, and FAS mutations may have arisen prior to domestication or early during the selection of cultivated tomato whereas the SUN mutation appeared to be a postdomestication event arising in Europe.
Rodríguez, GR. Muños, S. Anderson, C. Sim, SC. Michel, A. Causse, M. Gardener, BB. Francis, D. van der Knaap, E.
Plant physiology.
2011.
156(1).
275-85.
Increase in tomato locule number is controlled by two single-nucleotide polymorphisms located near WUSCHEL.
Plant physiology (2011)
Show / hide abstract
Show / hide abstract
In tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit, the number of locules (cavities containing seeds that are derived from carpels) varies from two to up to 10 or more. Locule number affects fruit shape and size and is controlled by several quantitative trait loci (QTLs). The large majority of the phenotypic variation is explained by two of these QTLs, fasciated (fas) and locule number (lc), that interact epistatically with one another. FAS has been cloned, and mutations in the gene are described as key factors leading to the increase in fruit size in modern varieties. Here, we report the map-based cloning of lc. The lc QTL includes a 1,600-bp region that is located 1,080 bp from the 3' end of WUSCHEL, which encodes a homeodomain protein that regulates stem cell fate in plants. The molecular evolution of lc showed a reduction of diversity in cultivated accessions with the exception of two single-nucleotide polymorphisms. These two single-nucleotide polymorphisms were shown to be responsible for the increase in locule number. An evolutionary model of locule number is proposed herein, suggesting that the fas mutation appeared after the mutation in the lc locus to confer the extreme high-locule-number phenotype.
Muños, S. Ranc, N. Botton, E. Bérard, A. Rolland, S. Duffé, P. Carretero, Y. Le Paslier, MC. Delalande, C. Bouzayen, M. Brunel, D. Causse, M.
Plant physiology.
2011.
156(4).
2244-54.
 Ontology annotations (0) Ontology annotations (0)
 Ontology annotations (0) Ontology annotations (0)
| [Add ontology annotations] |
[loading...]
 Related views Related views
 Related views Related views
|
none found
| User comments |
Please wait, checking for comments. (If comments do not show up, access them here)
Your Lists
Public Lists
List Contents
List Validation Report: Failed
Elements not found:
Optional: Add Missing Accessions to A List
Mismatched case
Click the Adjust Case button to align the case in the list with what is in the database.
Multiple mismatched case
Items listed here have mulitple case mismatches and must be fixed manually. If accessions need to be merged, contact the database directly.
List elements matching a synonym
Multiple synonym matches
Fuzzy Search Results
Synonym Search Results
Available Seedlots
Your Datasets
Public Datasets
Dataset Contents
Dataset Validation Failed
Elements not found:
Your Calendar
Having trouble viewing events on the calendar?
Are you associated with the breeding program you are interested in viewing?
Add New Event
Event Info
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Project Name: | |
| Start Date: | |
| End Date: | |
| Event Type: | |
| Event Description: | |
| Event Web URL: |
Edit Event
Login
Forgot Username
If you've forgotten your username, enter your email address below. An email will be sent with any account username(s) associated with your email address.
Reset Password
To reset your password, please enter your email address. A link will be sent to that address with a link that will enable you to reset your password.
Create New User
Working